Product Description
China Wholesale Price Stainless Steel Slotted Knurled High Cylinder Head Captive Capstan Panel Screws
| Item | Capstan Screw |
| Size | M3-M10 |
| Length | 10-200mm |
| Material | Stainless Steel 304/316, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel |
| Standard | DIN, ASME, BS, JIS, AS, EN, GB for option |
| Finish | Passivation, Plain,Galvanized, Nickel Plated, Balck Oxide, Gold Plated, Bronze Plated |
| Delivery Time | 3-15 days |
| Sample | Free |
| OEM | Available |
| Bolt | Screw | Nut | Washer |
| Rivet | Anchor | Pin | Hex Bolt |
| Drywall Screw | Hex Nut | Wedge Anchor | Flat Washer |
Q: What’s your product range?
A: Our product cover Bolts, Screws, Nuts, Washers, Spring ,Rivet, Anchor, Nail, CNC parts and so on.
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: 3 days for stock items,7-15 days for production.
Q: How do you control your quality.
A: QC on-line inspection and final inspection before delivery. 6S management. MTC and Quality Report can be provide.
Q: Could you provide free samples?
A: Yes, we could offer free samples for the items in stock, just need to pay shipping cost, it can be refunded to your orders.
Q: Do you accept small order?
A: Sure, we can accept small orders if we have stock of the specification which you need..
Q: What is your packing ?
A: 20-25kg for 1 carton,36 or 48 cartons for 1 pallet. One pallets is about 900-960kg. Customized carton and Customer’s logo is available.
Q: What is your payment term?
A: We can accept T/T, L/C for bulk order. Paypal and Western Union for small order or sample order.
Made-in-China Online payment is available.
Q: Do you accept customized order?
A: Yes, we can produce according to sample or drawing.
| Material: | Stainless Steel/Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Type: | Round Head |
| Groove: | Slotted |
| Head Style: | Cylinder Head |
| Standard: | DIN, GB, ANSI, JIS |
| Grade: | A2-70, A4-80, 4.8, 8.8 |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
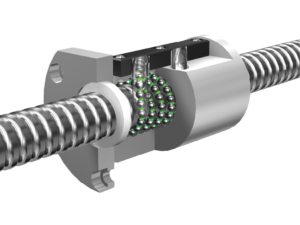
What role do lead screws play in ensuring proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies?
Lead screws play a crucial role in ensuring proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies. They provide a reliable means of applying axial force to securely fasten components together. Here’s how lead screws contribute to alignment and tightness:
Alignment:
Lead screws aid in achieving proper alignment in mechanical assemblies through the following mechanisms:
- Linear Motion: Lead screws convert rotary motion into linear motion, allowing for controlled movement and alignment of components. By rotating the lead screw, the connected nut or threaded component moves along the screw’s axis, enabling precise positioning and alignment of the assembly.
- Thread Engagement: The mating threads of the lead screw and nut provide a positive mechanical connection. As the nut moves along the screw, the threads engage tightly, ensuring accurate alignment between the screw and the nut. This thread engagement helps maintain the desired position and alignment of components within the assembly.
- Guidance and Support: Lead screws often incorporate guidance mechanisms, such as linear bearings or sliding surfaces, to ensure smooth and accurate linear motion. These guidance systems help prevent lateral movement, minimize misalignment, and maintain the intended trajectory of the assembly, improving overall alignment.
- Positioning Accuracy: Lead screws offer precise positioning capabilities, allowing for the accurate alignment of components. The thread pitch and design, combined with the rotational input, enable controlled linear movement and positioning. This precision is critical in applications where proper alignment is essential for optimal performance and functionality.
Tightness:
Lead screws contribute to achieving tightness and secure fastening in mechanical assemblies through the following means:
- Axial Force Application: Lead screws transmit axial force to clamp or tighten components together. By rotating the lead screw, the axial force is applied through the nut or threaded component, generating a clamping action that holds the assembly tightly. This axial force helps prevent loosening, vibration, or unintended movement of the connected components.
- Self-Locking Capability: Lead screws possess a self-locking characteristic, which means they can hold their position without the need for additional locking mechanisms. The friction between the mating threads provides resistance to back-driving and helps maintain the tightness of the assembly. This self-locking property ensures that the assembly remains securely fastened, even in the absence of continuous power input.
- Thread Friction: The friction between the mating threads of the lead screw and nut contributes to the tightness of the assembly. When properly lubricated, the thread friction helps increase the resistance to loosening or undesired movement. By controlling the thread friction, the tightness of the assembly can be optimized to meet the specific requirements of the application.
- Preload Adjustment: Lead screws allow for preload adjustment, which is the intentional application of axial force to achieve a desired level of tightness. Preload can be applied by adjusting the initial position of the nut along the lead screw or by incorporating preload mechanisms, such as spring washers or Belleville washers. Preload optimization ensures that the assembly remains tight and secure, even under varying loads or external disturbances.
Overall, lead screws provide a reliable means of achieving proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies. Their linear motion capabilities, thread engagement, guidance mechanisms, positioning accuracy, axial force application, self-locking capability, and preload adjustability all contribute to ensuring the stability, alignment, and tightness of the assembled components.
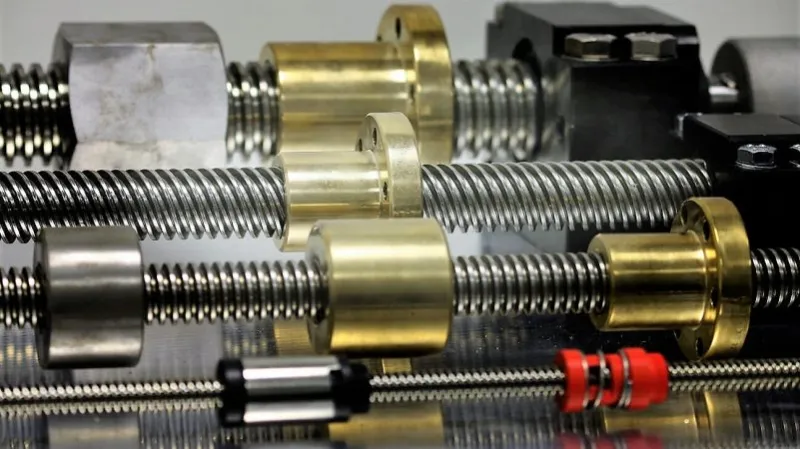

What are the signs that indicate a need for lead screw replacement or maintenance, and how can they be diagnosed?
Lead screws, like any mechanical component, may require replacement or maintenance over time due to wear, damage, or performance degradation. Recognizing the signs of potential issues and diagnosing them accurately is essential for timely intervention. Here are some common signs that indicate a need for lead screw replacement or maintenance, along with diagnostic methods:
- Increased Backlash: An increase in backlash, which is the clearance or play between the lead screw and nut, can signify wear or mechanical issues. Excessive backlash can result in decreased accuracy and precision. Diagnosis: Backlash can be measured using specialized tools, such as dial indicators or laser displacement sensors. Comparing the current backlash with the manufacturer’s specifications can help determine if maintenance or replacement is necessary.
- Unusual Noise or Vibration: Unusual noises, vibrations, or excessive mechanical resonance during operation can indicate misalignment, worn components, or inadequate lubrication. Diagnosis: Careful observation and listening during operation can help identify abnormal noise or vibration. Inspecting the lead screw for signs of wear, checking alignment, and ensuring proper lubrication can help diagnose the underlying issue.
- Reduced Accuracy or Repeatability: If a lead screw system starts exhibiting decreased accuracy or repeatability in positioning, it may indicate wear, misalignment, or damaged components. Diagnosis: Conducting precision tests or comparing the system’s actual position with the desired position can help identify any inconsistencies. Inspecting the lead screw, nut, or associated components for signs of wear or damage can provide further insights.
- Increased Friction or Sticking: If the lead screw system experiences increased friction or sticking during operation, it may indicate inadequate lubrication, contamination, or worn components. Diagnosis: Observing the smoothness of the lead screw’s movement and checking for signs of lubrication deficiency or contamination can help diagnose the issue. Cleaning the lead screw and applying appropriate lubrication may resolve minor friction-related problems.
- Visible Wear or Damage: Visual inspection of the lead screw and nut may reveal signs of wear, corrosion, or physical damage. This can include worn threads, scoring, pitting, or deformation. Diagnosis: Regular visual inspection of the lead screw system is important to identify visible signs of wear or damage. If significant wear or damage is observed, replacement or repair may be necessary.
- Inconsistent or Jerky Movement: If the lead screw system exhibits inconsistent or jerky movement instead of smooth and controlled motion, it may indicate misalignment, binding, or damaged components. Diagnosis: Careful observation of the system’s movement, checking for misalignment, and inspecting the lead screw, nut, or associated bearings for signs of binding or damage can help diagnose the issue.
It’s important to note that proper diagnosis and decision-making regarding lead screw replacement or maintenance may require the expertise of qualified technicians or engineers familiar with the specific application and system requirements. Following manufacturer guidelines, maintenance schedules, and seeking professional assistance can help ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate actions to maintain or replace the lead screw when necessary.

In what industries or applications are lead screws commonly utilized?
Lead screws are commonly utilized in various industries and applications that require precise linear motion, positioning, or adjustment of components. Here are some of the industries and applications where lead screws are frequently used:
- CNC Machining: Lead screws play a vital role in computer numerical control (CNC) machines. They are used in the linear motion systems of CNC mills, lathes, and routers to position and move the cutting tools or workpieces with high accuracy and repeatability.
- 3D Printing: Lead screws are widely employed in 3D printers to control the movement of the print head or build platform. They enable precise positioning of the print head, ensuring accurate layer-by-layer deposition of the printing material.
- Robotics: Lead screws find extensive use in robotic systems for various applications. They are utilized in robotic arms to control the movement and positioning of the end effectors or grippers. Lead screws also enable precise linear motion in robot joints, allowing for accurate and controlled robotic movements.
- Medical Equipment: Lead screws are employed in medical equipment and devices that require precise linear motion control. They can be found in medical imaging systems, laboratory automation equipment, surgical robots, patient positioning systems, and other medical devices.
- Industrial Automation: Lead screws are utilized in industrial automation applications for precise positioning and linear motion control. They are commonly found in assembly lines, packaging machines, material handling systems, and automated testing equipment.
- Aerospace and Aviation: Lead screws find use in aerospace and aviation applications that require accurate control of movable components. They can be found in aircraft controls, navigation systems, satellite positioning mechanisms, and aerospace testing equipment.
- Optics and Photonics: Lead screws are utilized in optics and photonics applications that require precise positioning or adjustment of optical components. They can be found in telescopes, microscopes, laser systems, and optical testing equipment.
- Industrial Machinery: Lead screws are commonly used in various types of industrial machinery. They can be found in equipment such as milling machines, drilling machines, grinding machines, textile machinery, printing presses, and many other types of machinery that require controlled linear motion.
- Automation in Home and Office: Lead screws are also utilized in automation systems for home and office applications. They can be found in motorized adjustable desks, automated window blinds, camera sliders, home theater systems, and other automated systems that require precise linear motion control.
These are just a few examples of the industries and applications where lead screws are commonly utilized. The versatility, precision, and reliability of lead screws make them a valuable component in numerous mechanical systems that require controlled linear motion or positioning of components.


editor by CX 2023-12-08