Product Description
Roller Screw for CNC Machine Lead Screw Trapezoidal Thread
Product Description
Specification:
|
Product Name |
Lead Screw |
|
Bearing steel, Gcr15 |
|
|
Precision |
C7,C5 |
|
Width |
4mm-100mm |
|
Length |
100mm-4000mm |
|
Advantage |
High precision, high speed, long life, high reliability, low noise |
|
Packing |
wooden box or according to customers’ demands |
Packaging & Shipping
Packaging Details:
1)Sample order packing by paper carton for saving freight charge;
2)bulk order sent by sea will be packed by film and wooden carton.
3) as customer’s requirements.
Company Profile
Company Information:
ZheJiang Sair Mechanical Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Co., Ltd is located at Xihu (West Lake) Dis. industrial zone Xihu (West Lake) Dis. County which is the beautiful Xihu (West Lake) Dis.
Water City and the famous painting and calligraphy village.The south is national road 308, the west is the national highway 105,
the north is HangZhou-HangZhou highway, so the position is very superior. It is 1 of the biggest linear manufacturers in China.
Certifications
FAQ
1. Q: How about the quality of your product?
A: 100% inspection during production.
Our products are certified to ISO9001-2008 international quality standards.
2. Q: What’s the delivery time?
A: For custom order, within 2000 meters,
Production time is 15days after confirmed every details.
3. Q: What’s your packing?
A: Our Normal packing is bulking in PE bag, and then into plywood Cartons.
We also can pack products according to your requirement.
4. Q: What about the warranty?
A: We are very confident in our products,
and we pack them very well to make sure the goods in well protection.
5.Q: Could you send me your catalogue and price list?
A: As we have more than hundreds of products,
it is really too hard to send all of catalogue and price list for you.
Please inform us the style you interested, we can offer the pricelist for your reference.
6.Q:There are a lot of companies which export bearings, why do you choose us?
A: As we are a genuine linear guide supplier since 2011.and we are really factory, you need not pay the profit for middlemen.
so we can offer you the lowest and competitive price .
Thanks for your valuable time !
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision: | C5 |
|---|---|
| Flange: | With Flange |
| Nut Number: | Single |
| Samples: |
US$ 15/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
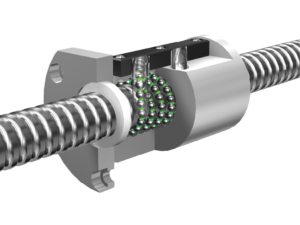
What role do lead screws play in ensuring proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies?
Lead screws play a crucial role in ensuring proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies. They provide a reliable means of applying axial force to securely fasten components together. Here’s how lead screws contribute to alignment and tightness:
Alignment:
Lead screws aid in achieving proper alignment in mechanical assemblies through the following mechanisms:
- Linear Motion: Lead screws convert rotary motion into linear motion, allowing for controlled movement and alignment of components. By rotating the lead screw, the connected nut or threaded component moves along the screw’s axis, enabling precise positioning and alignment of the assembly.
- Thread Engagement: The mating threads of the lead screw and nut provide a positive mechanical connection. As the nut moves along the screw, the threads engage tightly, ensuring accurate alignment between the screw and the nut. This thread engagement helps maintain the desired position and alignment of components within the assembly.
- Guidance and Support: Lead screws often incorporate guidance mechanisms, such as linear bearings or sliding surfaces, to ensure smooth and accurate linear motion. These guidance systems help prevent lateral movement, minimize misalignment, and maintain the intended trajectory of the assembly, improving overall alignment.
- Positioning Accuracy: Lead screws offer precise positioning capabilities, allowing for the accurate alignment of components. The thread pitch and design, combined with the rotational input, enable controlled linear movement and positioning. This precision is critical in applications where proper alignment is essential for optimal performance and functionality.
Tightness:
Lead screws contribute to achieving tightness and secure fastening in mechanical assemblies through the following means:
- Axial Force Application: Lead screws transmit axial force to clamp or tighten components together. By rotating the lead screw, the axial force is applied through the nut or threaded component, generating a clamping action that holds the assembly tightly. This axial force helps prevent loosening, vibration, or unintended movement of the connected components.
- Self-Locking Capability: Lead screws possess a self-locking characteristic, which means they can hold their position without the need for additional locking mechanisms. The friction between the mating threads provides resistance to back-driving and helps maintain the tightness of the assembly. This self-locking property ensures that the assembly remains securely fastened, even in the absence of continuous power input.
- Thread Friction: The friction between the mating threads of the lead screw and nut contributes to the tightness of the assembly. When properly lubricated, the thread friction helps increase the resistance to loosening or undesired movement. By controlling the thread friction, the tightness of the assembly can be optimized to meet the specific requirements of the application.
- Preload Adjustment: Lead screws allow for preload adjustment, which is the intentional application of axial force to achieve a desired level of tightness. Preload can be applied by adjusting the initial position of the nut along the lead screw or by incorporating preload mechanisms, such as spring washers or Belleville washers. Preload optimization ensures that the assembly remains tight and secure, even under varying loads or external disturbances.
Overall, lead screws provide a reliable means of achieving proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies. Their linear motion capabilities, thread engagement, guidance mechanisms, positioning accuracy, axial force application, self-locking capability, and preload adjustability all contribute to ensuring the stability, alignment, and tightness of the assembled components.

How do electronic or computer-controlled components integrate with lead screws in modern applications?
In modern applications, electronic or computer-controlled components play a crucial role in integrating with lead screws to enhance functionality, precision, and automation. These components enable advanced control, monitoring, and feedback capabilities, allowing for more efficient and accurate operation of systems incorporating lead screws. Here are some ways electronic or computer-controlled components integrate with lead screws in modern applications:
- Position Control: Electronic control systems can precisely control the position of the lead screw by monitoring and adjusting the rotational movement of the motor driving the screw. Position feedback sensors, such as encoders or linear scales, provide real-time information about the screw’s position, allowing the control system to accurately position the load. This integration enables precise positioning and highly repeatable motion control in applications such as CNC machinery, 3D printers, or robotic systems.
- Speed and Velocity Control: Electronic control systems can regulate the speed and velocity of the lead screw by controlling the motor’s rotational speed. By adjusting the motor speed, the control system can achieve specific linear speeds or velocity profiles along the length of the lead screw. This integration is particularly useful in applications where controlled acceleration, deceleration, or dynamic speed changes are required, such as automated manufacturing processes or motion control systems.
- Force and Torque Control: In some applications, it is necessary to control the force or torque applied by the lead screw. Electronic control systems can monitor and adjust the motor’s current or voltage to regulate the applied force or torque. This integration allows for precise force control, load balancing, or torque limiting in applications such as material testing machines, automated assembly systems, or lifting mechanisms.
- Automation and Synchronization: Electronic or computer-controlled components facilitate the automation and synchronization of multiple lead screws or other mechanical components. Through centralized control, these components can coordinate the movements of multiple lead screws, ensuring precise and synchronized motion. This integration is commonly used in complex systems with multiple axes of motion, such as multi-axis CNC machines or robotic systems.
- Monitoring and Diagnostics: Electronic control systems can monitor the operating parameters of lead screws, such as temperature, vibration, or load conditions. By integrating sensors and monitoring algorithms, the control system can detect abnormal conditions, provide real-time feedback, and trigger appropriate actions, such as alerting maintenance personnel or implementing protective measures. This integration enhances system reliability, prevents failures, and enables predictive maintenance in applications where lead screw performance is critical.
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Electronic or computer-controlled components often provide a user interface through which operators can interact with the lead screw system. HMIs allow operators to input commands, monitor system status, and receive feedback. This integration simplifies system operation, enables parameter adjustments, and facilitates troubleshooting or diagnostics.
In summary, electronic or computer-controlled components play a vital role in integrating with lead screws in modern applications. Position control, speed and velocity control, force and torque control, automation and synchronization, monitoring and diagnostics, and human-machine interface capabilities enhance the functionality, precision, and automation of systems incorporating lead screws. This integration enables advanced control, improved performance, and enhanced operational capabilities in various industries and applications.

In what industries or applications are lead screws commonly utilized?
Lead screws are commonly utilized in various industries and applications that require precise linear motion, positioning, or adjustment of components. Here are some of the industries and applications where lead screws are frequently used:
- CNC Machining: Lead screws play a vital role in computer numerical control (CNC) machines. They are used in the linear motion systems of CNC mills, lathes, and routers to position and move the cutting tools or workpieces with high accuracy and repeatability.
- 3D Printing: Lead screws are widely employed in 3D printers to control the movement of the print head or build platform. They enable precise positioning of the print head, ensuring accurate layer-by-layer deposition of the printing material.
- Robotics: Lead screws find extensive use in robotic systems for various applications. They are utilized in robotic arms to control the movement and positioning of the end effectors or grippers. Lead screws also enable precise linear motion in robot joints, allowing for accurate and controlled robotic movements.
- Medical Equipment: Lead screws are employed in medical equipment and devices that require precise linear motion control. They can be found in medical imaging systems, laboratory automation equipment, surgical robots, patient positioning systems, and other medical devices.
- Industrial Automation: Lead screws are utilized in industrial automation applications for precise positioning and linear motion control. They are commonly found in assembly lines, packaging machines, material handling systems, and automated testing equipment.
- Aerospace and Aviation: Lead screws find use in aerospace and aviation applications that require accurate control of movable components. They can be found in aircraft controls, navigation systems, satellite positioning mechanisms, and aerospace testing equipment.
- Optics and Photonics: Lead screws are utilized in optics and photonics applications that require precise positioning or adjustment of optical components. They can be found in telescopes, microscopes, laser systems, and optical testing equipment.
- Industrial Machinery: Lead screws are commonly used in various types of industrial machinery. They can be found in equipment such as milling machines, drilling machines, grinding machines, textile machinery, printing presses, and many other types of machinery that require controlled linear motion.
- Automation in Home and Office: Lead screws are also utilized in automation systems for home and office applications. They can be found in motorized adjustable desks, automated window blinds, camera sliders, home theater systems, and other automated systems that require precise linear motion control.
These are just a few examples of the industries and applications where lead screws are commonly utilized. The versatility, precision, and reliability of lead screws make them a valuable component in numerous mechanical systems that require controlled linear motion or positioning of components.


editor by CX 2024-03-15