Product Description
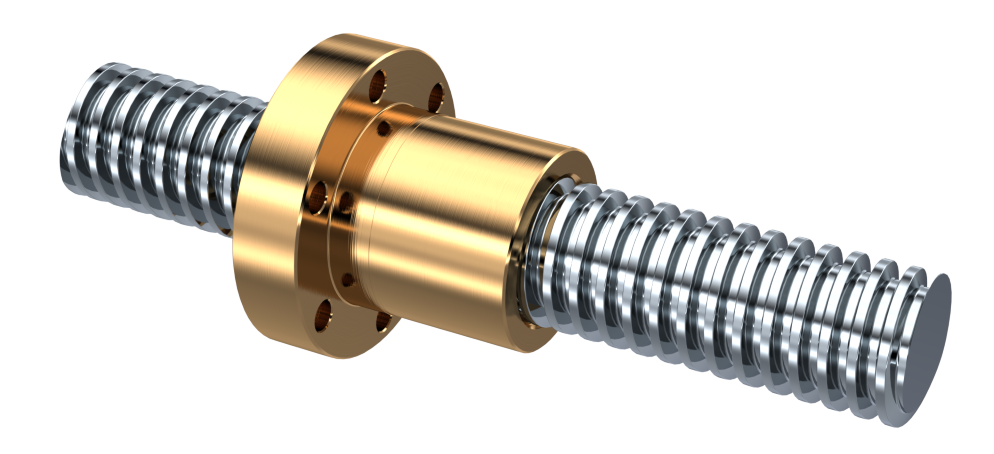
Roller Screw for CNC Machine Lead Screw Trapezoidal Thread
Product Description
Specification:
|
Product Name |
Lead Screw |
|
Bearing steel, Gcr15 |
|
|
Precision |
C7,C5 |
|
Width |
4mm-100mm |
|
Length |
100mm-4000mm |
|
Advantage |
High precision, high speed, long life, high reliability, low noise |
|
Packing |
wooden box or according to customers’ demands |
Packaging & Shipping
Packaging Details:
1)Sample order packing by paper carton for saving freight charge;
2)bulk order sent by sea will be packed by film and wooden carton.
3) as customer’s requirements.
Company Profile
Company Information:
ZheJiang Sair Mechanical Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Co., Ltd is located at Xihu (West Lake) Dis. industrial zone Xihu (West Lake) Dis. County which is the beautiful Xihu (West Lake) Dis.
Water City and the famous painting and calligraphy village.The south is national road 308, the west is the national highway 105,
the north is HangZhou-HangZhou highway, so the position is very superior. It is 1 of the biggest linear manufacturers in China.
Certifications
FAQ
1. Q: How about the quality of your product?
A: 100% inspection during production.
Our products are certified to ISO9001-2008 international quality standards.
2. Q: What’s the delivery time?
A: For custom order, within 2000 meters,
Production time is 15days after confirmed every details.
3. Q: What’s your packing?
A: Our Normal packing is bulking in PE bag, and then into plywood Cartons.
We also can pack products according to your requirement.
4. Q: What about the warranty?
A: We are very confident in our products,
and we pack them very well to make sure the goods in well protection.
5.Q: Could you send me your catalogue and price list?
A: As we have more than hundreds of products,
it is really too hard to send all of catalogue and price list for you.
Please inform us the style you interested, we can offer the pricelist for your reference.
6.Q:There are a lot of companies which export bearings, why do you choose us?
A: As we are a genuine linear guide supplier since 2011.and we are really factory, you need not pay the profit for middlemen.
so we can offer you the lowest and competitive price .
Thanks for your valuable time !
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision: | C5 |
|---|---|
| Flange: | With Flange |
| Nut Number: | Single |
| Samples: |
US$ 15/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
Can you provide examples of products or machinery that use lead screws for precise positioning?
Lead screws are widely utilized in various products and machinery that require precise positioning. Here are some examples of products and machinery that commonly use lead screws for precise positioning:
- CNC Machines: Computer numerical control (CNC) machines, including CNC mills, lathes, and routers, use lead screws to precisely position the cutting tools or workpieces. Lead screws enable accurate and repeatable movement in the linear motion systems of these machines, allowing for precise machining operations.
- 3D Printers: Lead screws are extensively used in 3D printers to control the movement of the print head or build platform. They enable precise positioning of the print head, ensuring accurate layer-by-layer deposition of the printing material, resulting in high-quality 3D prints.
- Robotics: Lead screws are integral to robotic systems that require precise positioning. They are used in robotic arms to control the movement and positioning of the end effectors or grippers. Lead screws provide accurate and controlled linear motion in robot joints, allowing for precise and coordinated movements in industrial, medical, and research robotics.
- Medical Imaging Systems: Lead screws are employed in medical imaging systems, such as computed tomography (CT) scanners and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, to precisely position the patient bed or gantry. This precise positioning is crucial for accurate imaging and diagnosis.
- Laboratory Automation Equipment: Lead screws are used in laboratory automation equipment, such as liquid handling robots and sample handling systems, for precise positioning and movement of samples, reagents, and labware. They ensure accurate and repeatable positioning required for various laboratory processes.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment: Lead screws are utilized in semiconductor manufacturing equipment, including wafer handling systems and lithography machines. They provide precise positioning and movement of wafers, masks, and other components critical for semiconductor fabrication processes.
- Camera Sliders: Lead screws are employed in camera sliders used in photography and videography applications. They enable smooth and precise linear motion of the camera along the slider, allowing for controlled tracking shots and precise camera positioning.
- Telescopes and Astronomy Equipment: Lead screws are utilized in telescopes and other astronomy equipment to precisely position optical components and achieve accurate tracking of celestial objects. They enable fine adjustments and precise pointing of telescopes for astronomical observations.
- Industrial Inspection Systems: Lead screws are used in industrial inspection systems, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and optical inspection systems, for precise movement and positioning of the inspection probes or cameras. This ensures accurate measurement and inspection of manufactured components.
These are just a few examples of the products and machinery that utilize lead screws for precise positioning. The versatility, accuracy, and reliability of lead screws make them a preferred choice in applications that require controlled linear motion and precise positioning of components.

What are the signs that indicate a need for lead screw replacement or maintenance, and how can they be diagnosed?
Lead screws, like any mechanical component, may require replacement or maintenance over time due to wear, damage, or performance degradation. Recognizing the signs of potential issues and diagnosing them accurately is essential for timely intervention. Here are some common signs that indicate a need for lead screw replacement or maintenance, along with diagnostic methods:
- Increased Backlash: An increase in backlash, which is the clearance or play between the lead screw and nut, can signify wear or mechanical issues. Excessive backlash can result in decreased accuracy and precision. Diagnosis: Backlash can be measured using specialized tools, such as dial indicators or laser displacement sensors. Comparing the current backlash with the manufacturer’s specifications can help determine if maintenance or replacement is necessary.
- Unusual Noise or Vibration: Unusual noises, vibrations, or excessive mechanical resonance during operation can indicate misalignment, worn components, or inadequate lubrication. Diagnosis: Careful observation and listening during operation can help identify abnormal noise or vibration. Inspecting the lead screw for signs of wear, checking alignment, and ensuring proper lubrication can help diagnose the underlying issue.
- Reduced Accuracy or Repeatability: If a lead screw system starts exhibiting decreased accuracy or repeatability in positioning, it may indicate wear, misalignment, or damaged components. Diagnosis: Conducting precision tests or comparing the system’s actual position with the desired position can help identify any inconsistencies. Inspecting the lead screw, nut, or associated components for signs of wear or damage can provide further insights.
- Increased Friction or Sticking: If the lead screw system experiences increased friction or sticking during operation, it may indicate inadequate lubrication, contamination, or worn components. Diagnosis: Observing the smoothness of the lead screw’s movement and checking for signs of lubrication deficiency or contamination can help diagnose the issue. Cleaning the lead screw and applying appropriate lubrication may resolve minor friction-related problems.
- Visible Wear or Damage: Visual inspection of the lead screw and nut may reveal signs of wear, corrosion, or physical damage. This can include worn threads, scoring, pitting, or deformation. Diagnosis: Regular visual inspection of the lead screw system is important to identify visible signs of wear or damage. If significant wear or damage is observed, replacement or repair may be necessary.
- Inconsistent or Jerky Movement: If the lead screw system exhibits inconsistent or jerky movement instead of smooth and controlled motion, it may indicate misalignment, binding, or damaged components. Diagnosis: Careful observation of the system’s movement, checking for misalignment, and inspecting the lead screw, nut, or associated bearings for signs of binding or damage can help diagnose the issue.
It’s important to note that proper diagnosis and decision-making regarding lead screw replacement or maintenance may require the expertise of qualified technicians or engineers familiar with the specific application and system requirements. Following manufacturer guidelines, maintenance schedules, and seeking professional assistance can help ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate actions to maintain or replace the lead screw when necessary.

How does a lead screw differ from other types of screws in terms of design and functionality?
A lead screw differs from other types of screws in terms of its design and functionality. Here’s a detailed explanation of the distinctions between lead screws and other screw types:
- Thread Design: Lead screws have a helical thread design, meaning the threads wrap around the screw’s cylindrical shaft in a continuous spiral. This helical thread allows for the conversion of rotary motion into linear motion. In contrast, other types of screws, such as machine screws or wood screws, typically have a straight or tapered thread design suited for fastening or joining applications.
- Linear Motion Conversion: The primary function of a lead screw is to convert rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa. It achieves this by utilizing the engagement between the helical threads on the screw and the matching threads on the nut. This capability makes lead screws suitable for applications requiring precise positioning, actuation, or adjustment of components along a linear path. In contrast, other screws are primarily used for fastening, joining, or securing objects together.
- Precision and Control: Lead screws offer precise control over linear movement due to their thread pitch and the ability to rotate the screw with precision. The pitch determines the linear distance the nut will travel for each revolution of the screw. This feature makes lead screws well-suited for applications that demand accurate positioning or adjustment. In contrast, other screws are not designed with the same level of precision or control over linear motion.
- Load Handling: Lead screws are designed to handle both axial loads (tension or compression forces) and torque. The helical threads and the engagement between the screw and nut distribute the load over a larger surface area, allowing lead screws to support and transfer significant loads. Other screw types, such as machine screws or wood screws, are primarily used for fastening and may not have the same load-bearing capabilities as lead screws.
- Applications: Lead screws find applications in various mechanical systems that require precise linear motion, such as CNC machines, 3D printers, robotic systems, and adjustable mechanisms. They are commonly used for positioning, actuation, or adjustment purposes. Conversely, other types of screws serve different purposes, such as machine screws used for fastening components together, wood screws for joining wooden materials, or self-tapping screws for creating threads in materials like metal or plastic.
Overall, the key differences between lead screws and other types of screws lie in their thread design, their ability to convert rotary motion to linear motion, the precision and control they offer, their load-handling capabilities, and the specific applications they are designed for. Understanding these distinctions is essential when selecting the appropriate screw type for a particular mechanical application.


editor by Dream 2024-05-06