Product Description
GLM Series Stepped Precision Ball Screw (C3/C5)
| Table of Shaft dia. and Lead combination for Precision Ball Screw | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lead (mm) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 32 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 63 | ||
| Shaft dia (mm) | 4 | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||||
| 5 | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||
| 8 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 10 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||
| 12 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||
| 13 | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||
| 20 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||
| 25 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||
| 28 | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 39 | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 48 | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 50 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||
| 60 | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 63 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 80 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||
| 100 | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||
| 120 | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 125 | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||||
| 160 | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||
| 200 | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||||
Accuracy class and axial clearance
Accuracy grade of GLM series(precision ball screw with single nut with metric thread) are based on C3 and C5(JIS B 1192-3). According to accuracy grade, Axial play 0(Preload :C3) and 0.005mm or less(C5).
Material & Surface Hardness
GLM series (precision ball screw with single nut with metric thread) of screw shaft screw material S55C (induction hardening), nut material SCM415H (carburizing and hardening), the surface hardness of the ball screw part is HRC58 or higher.
Application:
1. Medical industry
2.Lithium battery industry
3.Solar photovoltaic industry
4. Semiconductor Industry
5. General industry machinery
6. Machine tool
7. Parking system
8. High-speed rail and aviation transportation equipment
9. 3C industry etc
Shaft End Shape
The shaft end shape of the GLM series (precision ball screws with single nut with metric thread) has been standardized.
Technical Drawing
Specification List
FACTORY DETAILED PROCESSING PHOTOS
HIGH QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEM
FAQ
1. Why choose CHINAMFG China?
Over the past 14 years, CHINAMFG has always insisted that “products and services” start from Japanese industry standards,taking ZheJiang standards as the bottom line, actively invest in the development of new transmission components and self-experiment and test. With the service tenet of “exceeding customer expectations”, establish a “trusted” partnership.
2. What is your main products ?
We are a leading manufacturer and distributor of linear motion components in China. Especially miniature size of Ball Screws and Linear Actuators and linear motion guideways. Our brand “KGG” stands for ” Know-how,” ” Great Quality,” and ” Good value” and our factory is located in the most advanced city in China: ZheJiang with the best equipment and sophisticated technology, completely strict quality control system. Our aim is to supply world leader class linear motion components but with most reasonable price in the world.
3. How to Custom-made (OEM/ODM)?
If you have a product drawing or a sample, please send to us, and we can custom-made the as your required. We will also provide our professional advices of the products to make the design to be more realized & maximize the performance.
4. When can I get the quotation?
We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are very urgent to get the price,please call us or tell us in your email so that we will regard your inquiry priority.
5. How can I get a sample to check the quality?
After confirmation of our quoted price, you can place the sample order. The sample will be started after you CHINAMFG back our detailed technical file.
6. What’s your payment terms?
Our payment terms is 30% deposit,balance 70% before shipment. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
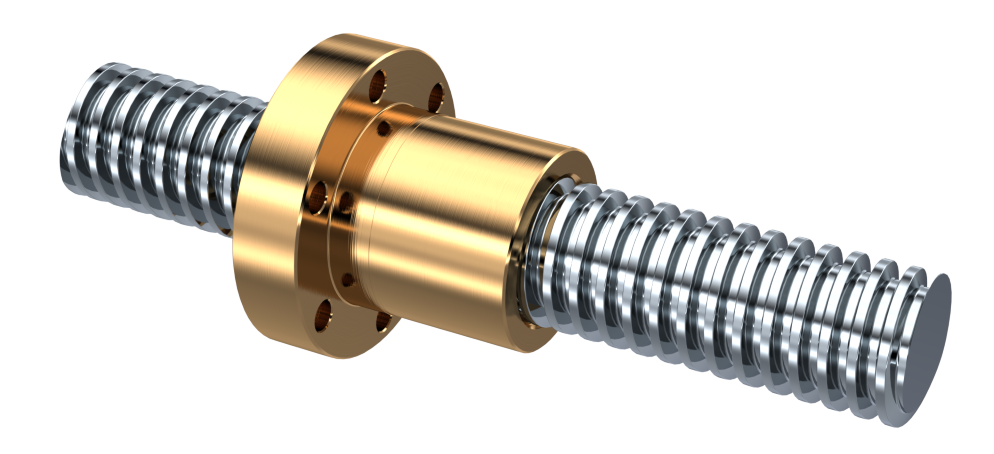
| Precision: | C3/C5 |
|---|---|
| Screw Diameter: | 12mm |
| Flange: | With Flange |
| Nut Number: | Single |
| Rows Number: | 4-Row |
| Nut Type: | Circulator |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
Can you provide examples of products or machinery that use lead screws for precise positioning?
Lead screws are widely utilized in various products and machinery that require precise positioning. Here are some examples of products and machinery that commonly use lead screws for precise positioning:
- CNC Machines: Computer numerical control (CNC) machines, including CNC mills, lathes, and routers, use lead screws to precisely position the cutting tools or workpieces. Lead screws enable accurate and repeatable movement in the linear motion systems of these machines, allowing for precise machining operations.
- 3D Printers: Lead screws are extensively used in 3D printers to control the movement of the print head or build platform. They enable precise positioning of the print head, ensuring accurate layer-by-layer deposition of the printing material, resulting in high-quality 3D prints.
- Robotics: Lead screws are integral to robotic systems that require precise positioning. They are used in robotic arms to control the movement and positioning of the end effectors or grippers. Lead screws provide accurate and controlled linear motion in robot joints, allowing for precise and coordinated movements in industrial, medical, and research robotics.
- Medical Imaging Systems: Lead screws are employed in medical imaging systems, such as computed tomography (CT) scanners and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, to precisely position the patient bed or gantry. This precise positioning is crucial for accurate imaging and diagnosis.
- Laboratory Automation Equipment: Lead screws are used in laboratory automation equipment, such as liquid handling robots and sample handling systems, for precise positioning and movement of samples, reagents, and labware. They ensure accurate and repeatable positioning required for various laboratory processes.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment: Lead screws are utilized in semiconductor manufacturing equipment, including wafer handling systems and lithography machines. They provide precise positioning and movement of wafers, masks, and other components critical for semiconductor fabrication processes.
- Camera Sliders: Lead screws are employed in camera sliders used in photography and videography applications. They enable smooth and precise linear motion of the camera along the slider, allowing for controlled tracking shots and precise camera positioning.
- Telescopes and Astronomy Equipment: Lead screws are utilized in telescopes and other astronomy equipment to precisely position optical components and achieve accurate tracking of celestial objects. They enable fine adjustments and precise pointing of telescopes for astronomical observations.
- Industrial Inspection Systems: Lead screws are used in industrial inspection systems, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and optical inspection systems, for precise movement and positioning of the inspection probes or cameras. This ensures accurate measurement and inspection of manufactured components.
These are just a few examples of the products and machinery that utilize lead screws for precise positioning. The versatility, accuracy, and reliability of lead screws make them a preferred choice in applications that require controlled linear motion and precise positioning of components.

Can you provide insights into the importance of proper lead screw installation and alignment?
Proper lead screw installation and alignment are crucial for ensuring the optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of lead screw systems. The installation and alignment process directly affects the system’s accuracy, efficiency, and overall functionality. Here are some key insights into the importance of proper lead screw installation and alignment:
- Accuracy and Precision: Proper installation and alignment are essential for achieving accurate and precise linear motion. Misalignment or incorrect installation can introduce angular errors, axial misalignment, or parallelism issues, leading to positioning errors and reduced system accuracy. By following the manufacturer’s guidelines and using appropriate alignment tools, the lead screw can be installed in a way that minimizes misalignment and ensures precise movement and positioning.
- Load Distribution: Correct alignment during installation helps distribute the load evenly along the length of the lead screw. Proper alignment ensures that the load is shared uniformly between the screw and the nut, preventing excessive stress on specific areas. Improved load distribution reduces the risk of premature wear, deformation, or failure of the lead screw and enhances the overall durability and load-carrying capacity of the system.
- Backlash and Efficiency: Proper installation and alignment contribute to minimizing backlash in lead screw systems. Backlash, which refers to the clearance between the screw and nut, can negatively impact system performance, precision, and efficiency. Misalignment can exacerbate backlash issues, resulting in reduced repeatability and accuracy. By aligning the lead screw correctly, the backlash can be minimized, improving system efficiency and eliminating potential sources of error.
- Reduced Friction and Wear: Accurate installation and alignment help reduce friction and wear between the lead screw and nut. Misalignment can cause the screw and nut to rub against each other unevenly, leading to increased friction, accelerated wear, and reduced system lifespan. Proper alignment ensures that the mating surfaces are in optimal contact, minimizing friction and wear, and improving the overall efficiency and longevity of the lead screw system.
- System Stability and Vibration: Proper installation and alignment contribute to system stability and reduced vibration. Misalignment can introduce vibrations, resonances, or oscillations in the lead screw system, affecting the overall performance and potentially causing excessive noise or system instability. By aligning the lead screw correctly, the system’s natural frequencies can be maintained within acceptable limits, improving stability, reducing vibrations, and enhancing the system’s overall operation.
- Maintenance and Service: Proper installation and alignment simplify maintenance and service procedures. When lead screws are installed and aligned accurately, routine maintenance tasks such as lubrication, inspection, or component replacement can be performed more efficiently. Access to critical components is improved, and troubleshooting potential issues becomes easier, reducing downtime and enhancing the overall serviceability of the lead screw system.
In conclusion, proper lead screw installation and alignment are of utmost importance for achieving optimal performance, accuracy, efficiency, and durability of lead screw systems. Accurate alignment minimizes positioning errors, improves load distribution, reduces backlash and friction, enhances system stability, and simplifies maintenance procedures. By following manufacturer guidelines and utilizing appropriate alignment techniques, the benefits of proper installation and alignment can be realized, ensuring the long-term reliability and performance of lead screw systems.

Can you describe the various types and configurations of lead screws available in the market?
Lead screws are available in various types and configurations to suit different applications and requirements. Here’s an overview of the common types and configurations of lead screws found in the market:
- Acme Lead Screws: Acme lead screws are one of the most widely used types. They have a trapezoidal thread profile with a 29-degree thread angle. Acme screws are known for their strength, durability, and high load-carrying capacity. They offer efficient linear motion conversion and are commonly used in applications that require heavy-duty and high-load capabilities.
- Ball Screws: Ball screws are precision lead screws that incorporate ball bearings between the screw and nut. The ball bearings reduce friction, allowing for smoother and more efficient linear motion. Ball screws offer high accuracy, low backlash, and excellent repeatability. They are commonly used in applications that require high precision, such as CNC machines, robotics, and semiconductor manufacturing equipment.
- Stub Acme Screws: Stub Acme screws are similar to Acme screws but have a shallower thread depth. They offer higher efficiency and smoother operation compared to Acme screws. Stub Acme screws are commonly used in applications where space is limited or when a lighter load capacity is required.
- Buttress Screws: Buttress screws have a thread profile with one flank at a 45-degree angle and the other flank perpendicular to the screw axis. This design provides high load-carrying capacity in one direction while allowing for easy movement in the opposite direction. Buttress screws are commonly used in applications that require the transmission of heavy axial loads in a single direction, such as presses or jacks.
- Multiple-Start Screws: Multiple-start screws have two or more threads wrapped around the screw shaft. This design allows for faster linear travel per revolution compared to single-start screws. Multiple-start screws are used in applications where higher linear speeds or quick linear positioning is required.
- Thread Forms: Apart from the specific types mentioned above, lead screws can also come in different thread forms to suit specific applications. Some common thread forms include square threads, triangular threads, and rounded threads. These thread forms offer variations in load-carrying capacity, efficiency, backlash, and cost, providing options to meet specific application requirements.
- Lead Screw Configurations: Lead screws can be found in various configurations depending on the specific application. Some configurations include:
- – Standard Lead Screws: These are the most common configurations with a cylindrical shaft and threads along its length.
- – Flanged Lead Screws: These lead screws have a flange at one or both ends, providing support and alignment in certain applications.
- – Anti-Backlash Lead Screws: These lead screws incorporate mechanisms to minimize or eliminate backlash, providing more precise linear motion control.
- – Customized Lead Screws: Lead screws can be customized to meet specific application requirements, such as specific dimensions, thread pitch, end machining, or material selection.
These are some of the common types and configurations of lead screws available in the market. The selection of the appropriate lead screw type depends on factors such as load requirements, precision needs, speed, backlash tolerance, and specific application constraints.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09