Product Description
GG Series Stepped Precision Ball Screw (C3/C5)
| Table of Shaft dia. and Lead combination for Precision Ball Screw | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lead (mm) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 32 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 63 | ||
| Shaft dia (mm) | 4 | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||||
| 5 | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||
| 8 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 10 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||
| 12 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||
| 13 | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||
| 20 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||
| 25 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||
| 28 | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 39 | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||
| 48 | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 50 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||
| 60 | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 63 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||
| 80 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||
| 100 | / | / | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||
| 120 | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 125 | / | / | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||||
| 160 | / | / | / | / | |||||||||||||||||||
| 200 | / | / | / | ||||||||||||||||||||
Accuracy class and axial clearance
Accuracy grade of GG series stepped precision ball screw are based on C3 and C5(JISB1192-3). According to accuracy grade, Axial play 0 (Preload :C3) and 0.005mm or less(C5).
Material & Surface Hardness
GG series stepped precision ball screw of screw shaft screw material S55C (induction hardening), nut material SCM415H (carburizing and hardening), the surface hardness of the ball screw part is HRC58 or higher.
Application:
1. Medical industry
2.Lithium battery industry
3.Solar photovoltaic industry
4. Semiconductor Industry
5. General industry machinery
6. Machine tool
7. Parking system
8. High-speed rail and aviation transportation equipment
9. 3C industry etc
Shaft End Shape
The shaft end shape of the GG series stepped precision ball screw has been standardized.
Technical Drawing
Specification List
FACTORY DETAILED PROCESSING PHOTOS
HIGH QUALITY CONTROL SYSTEM
FAQ
1. Why choose CHINAMFG China?
Over the past 14 years, CHINAMFG has always insisted that “products and services” start from Japanese industry standards,taking ZheJiang standards as the bottom line, actively invest in the development of new transmission components and self-experiment and test. With the service tenet of “exceeding customer expectations”, establish a “trusted” partnership.
2. What is your main products ?
We are a leading manufacturer and distributor of linear motion components in China. Especially miniature size of Ball Screws and Linear Actuators and linear motion guideways. Our brand “KGG” stands for ” Know-how,” ” Great Quality,” and ” Good value” and our factory is located in the most advanced city in China: ZheJiang with the best equipment and sophisticated technology, completely strict quality control system. Our aim is to supply world leader class linear motion components but with most reasonable price in the world.
3. How to Custom-made (OEM/ODM)?
If you have a product drawing or a sample, please send to us, and we can custom-made the as your required. We will also provide our professional advices of the products to make the design to be more realized & maximize the performance.
4. When can I get the quotation?
We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are very urgent to get the price,please call us or tell us in your email so that we will regard your inquiry priority.
5. How can I get a sample to check the quality?
After confirmation of our quoted price, you can place the sample order. The sample will be started after you CHINAMFG back our detailed technical file.
6. What’s your payment terms?
Our payment terms is 30% deposit,balance 70% before shipment. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
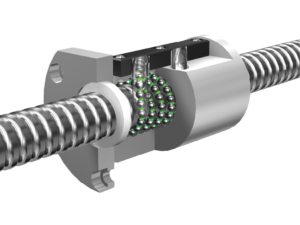
| Precision: | C3/C5 |
|---|---|
| Screw Diameter: | 12mm |
| Flange: | With Flange |
| Nut Number: | Single |
| Rows Number: | 4-Row |
| Nut Type: | Circulator |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
What role do lead screws play in ensuring proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies?
Lead screws play a crucial role in ensuring proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies. They provide a reliable means of applying axial force to securely fasten components together. Here’s how lead screws contribute to alignment and tightness:
Alignment:
Lead screws aid in achieving proper alignment in mechanical assemblies through the following mechanisms:
- Linear Motion: Lead screws convert rotary motion into linear motion, allowing for controlled movement and alignment of components. By rotating the lead screw, the connected nut or threaded component moves along the screw’s axis, enabling precise positioning and alignment of the assembly.
- Thread Engagement: The mating threads of the lead screw and nut provide a positive mechanical connection. As the nut moves along the screw, the threads engage tightly, ensuring accurate alignment between the screw and the nut. This thread engagement helps maintain the desired position and alignment of components within the assembly.
- Guidance and Support: Lead screws often incorporate guidance mechanisms, such as linear bearings or sliding surfaces, to ensure smooth and accurate linear motion. These guidance systems help prevent lateral movement, minimize misalignment, and maintain the intended trajectory of the assembly, improving overall alignment.
- Positioning Accuracy: Lead screws offer precise positioning capabilities, allowing for the accurate alignment of components. The thread pitch and design, combined with the rotational input, enable controlled linear movement and positioning. This precision is critical in applications where proper alignment is essential for optimal performance and functionality.
Tightness:
Lead screws contribute to achieving tightness and secure fastening in mechanical assemblies through the following means:
- Axial Force Application: Lead screws transmit axial force to clamp or tighten components together. By rotating the lead screw, the axial force is applied through the nut or threaded component, generating a clamping action that holds the assembly tightly. This axial force helps prevent loosening, vibration, or unintended movement of the connected components.
- Self-Locking Capability: Lead screws possess a self-locking characteristic, which means they can hold their position without the need for additional locking mechanisms. The friction between the mating threads provides resistance to back-driving and helps maintain the tightness of the assembly. This self-locking property ensures that the assembly remains securely fastened, even in the absence of continuous power input.
- Thread Friction: The friction between the mating threads of the lead screw and nut contributes to the tightness of the assembly. When properly lubricated, the thread friction helps increase the resistance to loosening or undesired movement. By controlling the thread friction, the tightness of the assembly can be optimized to meet the specific requirements of the application.
- Preload Adjustment: Lead screws allow for preload adjustment, which is the intentional application of axial force to achieve a desired level of tightness. Preload can be applied by adjusting the initial position of the nut along the lead screw or by incorporating preload mechanisms, such as spring washers or Belleville washers. Preload optimization ensures that the assembly remains tight and secure, even under varying loads or external disturbances.
Overall, lead screws provide a reliable means of achieving proper alignment and tightness in mechanical assemblies. Their linear motion capabilities, thread engagement, guidance mechanisms, positioning accuracy, axial force application, self-locking capability, and preload adjustability all contribute to ensuring the stability, alignment, and tightness of the assembled components.
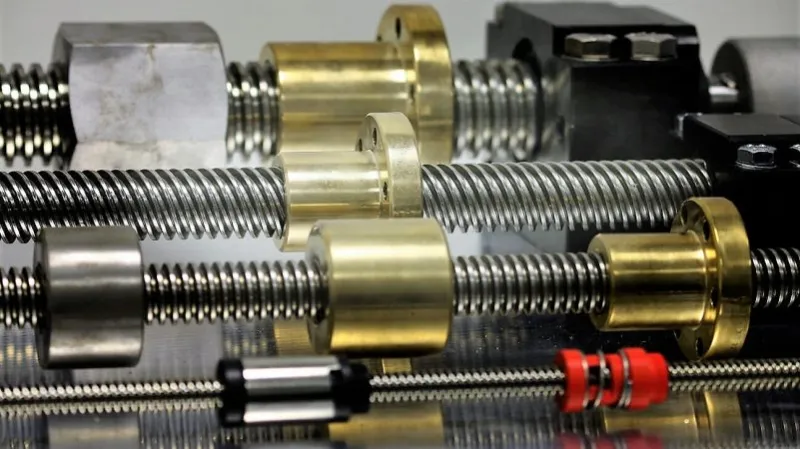

What are the signs that indicate a need for lead screw replacement or maintenance, and how can they be diagnosed?
Lead screws, like any mechanical component, may require replacement or maintenance over time due to wear, damage, or performance degradation. Recognizing the signs of potential issues and diagnosing them accurately is essential for timely intervention. Here are some common signs that indicate a need for lead screw replacement or maintenance, along with diagnostic methods:
- Increased Backlash: An increase in backlash, which is the clearance or play between the lead screw and nut, can signify wear or mechanical issues. Excessive backlash can result in decreased accuracy and precision. Diagnosis: Backlash can be measured using specialized tools, such as dial indicators or laser displacement sensors. Comparing the current backlash with the manufacturer’s specifications can help determine if maintenance or replacement is necessary.
- Unusual Noise or Vibration: Unusual noises, vibrations, or excessive mechanical resonance during operation can indicate misalignment, worn components, or inadequate lubrication. Diagnosis: Careful observation and listening during operation can help identify abnormal noise or vibration. Inspecting the lead screw for signs of wear, checking alignment, and ensuring proper lubrication can help diagnose the underlying issue.
- Reduced Accuracy or Repeatability: If a lead screw system starts exhibiting decreased accuracy or repeatability in positioning, it may indicate wear, misalignment, or damaged components. Diagnosis: Conducting precision tests or comparing the system’s actual position with the desired position can help identify any inconsistencies. Inspecting the lead screw, nut, or associated components for signs of wear or damage can provide further insights.
- Increased Friction or Sticking: If the lead screw system experiences increased friction or sticking during operation, it may indicate inadequate lubrication, contamination, or worn components. Diagnosis: Observing the smoothness of the lead screw’s movement and checking for signs of lubrication deficiency or contamination can help diagnose the issue. Cleaning the lead screw and applying appropriate lubrication may resolve minor friction-related problems.
- Visible Wear or Damage: Visual inspection of the lead screw and nut may reveal signs of wear, corrosion, or physical damage. This can include worn threads, scoring, pitting, or deformation. Diagnosis: Regular visual inspection of the lead screw system is important to identify visible signs of wear or damage. If significant wear or damage is observed, replacement or repair may be necessary.
- Inconsistent or Jerky Movement: If the lead screw system exhibits inconsistent or jerky movement instead of smooth and controlled motion, it may indicate misalignment, binding, or damaged components. Diagnosis: Careful observation of the system’s movement, checking for misalignment, and inspecting the lead screw, nut, or associated bearings for signs of binding or damage can help diagnose the issue.
It’s important to note that proper diagnosis and decision-making regarding lead screw replacement or maintenance may require the expertise of qualified technicians or engineers familiar with the specific application and system requirements. Following manufacturer guidelines, maintenance schedules, and seeking professional assistance can help ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate actions to maintain or replace the lead screw when necessary.
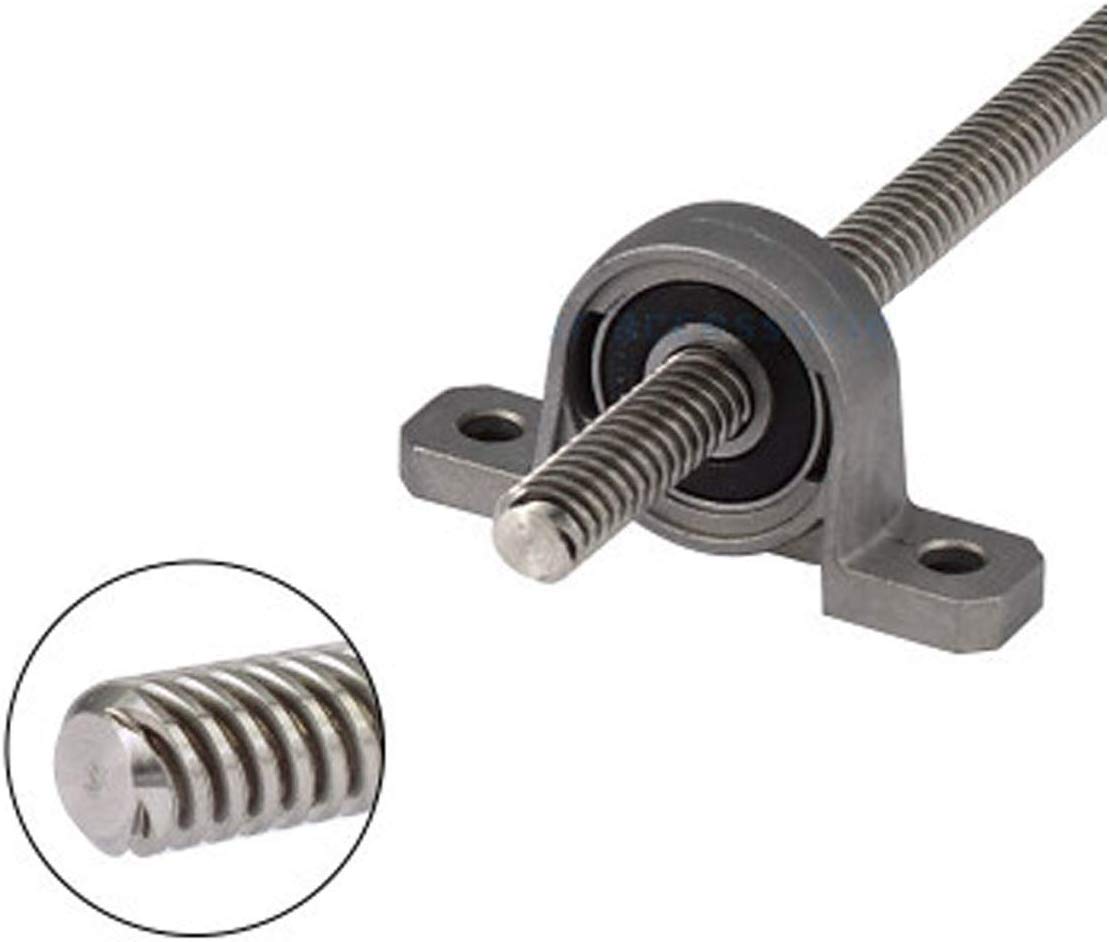

How does a lead screw differ from other types of screws in terms of design and functionality?
A lead screw differs from other types of screws in terms of its design and functionality. Here’s a detailed explanation of the distinctions between lead screws and other screw types:
- Thread Design: Lead screws have a helical thread design, meaning the threads wrap around the screw’s cylindrical shaft in a continuous spiral. This helical thread allows for the conversion of rotary motion into linear motion. In contrast, other types of screws, such as machine screws or wood screws, typically have a straight or tapered thread design suited for fastening or joining applications.
- Linear Motion Conversion: The primary function of a lead screw is to convert rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa. It achieves this by utilizing the engagement between the helical threads on the screw and the matching threads on the nut. This capability makes lead screws suitable for applications requiring precise positioning, actuation, or adjustment of components along a linear path. In contrast, other screws are primarily used for fastening, joining, or securing objects together.
- Precision and Control: Lead screws offer precise control over linear movement due to their thread pitch and the ability to rotate the screw with precision. The pitch determines the linear distance the nut will travel for each revolution of the screw. This feature makes lead screws well-suited for applications that demand accurate positioning or adjustment. In contrast, other screws are not designed with the same level of precision or control over linear motion.
- Load Handling: Lead screws are designed to handle both axial loads (tension or compression forces) and torque. The helical threads and the engagement between the screw and nut distribute the load over a larger surface area, allowing lead screws to support and transfer significant loads. Other screw types, such as machine screws or wood screws, are primarily used for fastening and may not have the same load-bearing capabilities as lead screws.
- Applications: Lead screws find applications in various mechanical systems that require precise linear motion, such as CNC machines, 3D printers, robotic systems, and adjustable mechanisms. They are commonly used for positioning, actuation, or adjustment purposes. Conversely, other types of screws serve different purposes, such as machine screws used for fastening components together, wood screws for joining wooden materials, or self-tapping screws for creating threads in materials like metal or plastic.
Overall, the key differences between lead screws and other types of screws lie in their thread design, their ability to convert rotary motion to linear motion, the precision and control they offer, their load-handling capabilities, and the specific applications they are designed for. Understanding these distinctions is essential when selecting the appropriate screw type for a particular mechanical application.


editor by Dream 2024-05-14